Dove vs Pigeon: Identification, Differences and Similarities
One of the most commonly asked questions about doves and pigeons is what are the differences that set them apart. Most people argue that these birds are the same while others believe that they’re completely different types of birds. So, what’s the truth? Are doves and pigeons the same?
Scientifically, there’s no difference between a dove and a pigeon and they’re all regarded as the same species of birds. However, there are some key differences between what people call doves and pigeons. Doves are smaller while pigeons are the larger species. Doves also have straighter tails while pigeons have more fanned-out tails.
In this article, we’ll discuss full details on the dove vs pigeon topic. We’ll discuss how to identify a dove or a pigeon and whether there exist any similarities or differences between these birds. By the time you’re done reading this post, you’ll have uncovered whether these birds are the same or completely different.
Dove vs Pigeon: Identification
Although we have said that doves and pigeons are the same bird species and have no scientific differences, they still have unique characteristics that set them apart as per human perception or culture.
The doves are generally considered noble and elegant birds, a symbol of purity, or bringers of peace. They’re generally regarded as being smaller than pigeons and are usually white in color.

Pigeons, on the other hand, are stocky birds that are usually kept as pets or ornamental birds, food sources, and even a trademark of the old Europe city squares. These birds are also regarded as disease vectors.
Pigeons were actively involved in the world wars where they were used to deliver messages or as spy device carriers.
As for the language part, the word pigeon comes from French while dove comes from Norse.
Dove vs Pigeon: Differences and similarities
Scientifically, there are no differences between doves and pigeons. They all belong to the same family (Columbidae or Columbids).
This family has more than 300 species of birds, some of which are commonly referred to as doves and others pigeons.
These two groups of birds don’t represent subfamilies and there’s absolutely no scientific clue that shows the dove and pigeon division. There also exists no zoological classification between doves and pigeons.
Sometimes, the two names are used interchangeably when referring to these birds.
For instance, the most famous member of this family, the rock pigeon (Columba livia) is also referred to as rock dove.
However, there are some notable differences between these two birds as discussed below:
Size
As we mentioned earlier, one of the distinct differences between what people call doves and pigeons is that the pigeons are generally bulkier and larger compared to the doves.
Take, for instance, the common wood pigeon. This bird weighs 48 to 550 and measures 40 to 42 cm in length. It also has a wingspan of around 75 to 08cm.

In comparison, the Eurasian collared dove, which is also native to Eurasian and lives within a similar range to the wood pigeon. This bird weighs around 200 grams and is approx. 32cm long. It has a wingspan of about 51 cm.
Still at it, the largest wild pigeon known to humankind is the Victoria Crowned Pigeon which weighs approx. 3,4kg (3400g) and has a length of around 75 to 85 cm.
The biggest domesticated pigeon is the giant runt pigeon which weighs up to 1.3kgs (1300g), is 55cm long, and has a wingspan of up to 110cm.
As for the doves, the smallest member of the Columbidae family is the common ground dove. Native to North America, this bird weighs 28 to 40 grams only and measures 15 to 18 cm (about the same size as the song sparrow).
Body shape
Both pigeons and doves feature a similar build; they feature rounded bodies with smallish round heads and short necks. They also have relatively short beaks.
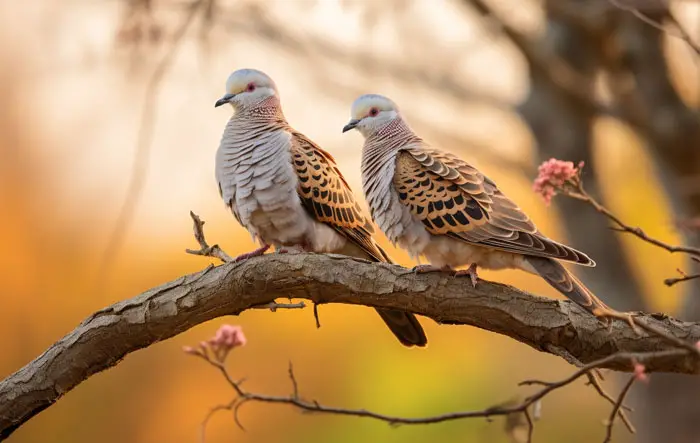

However, the larger and stockier columbids are often regarded as the pigeons while the smaller and slimmer members get the dove title.
Doves also tend to feature thinner and longer tails that spread more during flight. This is unlike the pigeon tails, which are usually stockier and shorter.
Behavior
The behavior of pigeons and doves usually depends on the species in question. As we said earlier, this bird family has over 300 species distributed across various ecological niches.
Therefore, their lifestyle tends to significantly differ from species to species. Some birds can be highly gregarious or solitary, semi-tame or friendly, migratory or sedentary, and so on.
Nevertheless, all the birds under the family Columbidae share several behavioral traits as outlined below:
- All doves and pigeons are diurnal, meaning they’re mostly active during the day and retire to their roosts at night. Some of the migratory species may however fly at night during migration.
- Most dove and pigeon species tend to become aggressive and territorial towards the same species as well as intruders during the mating season.
- All doves and pigeons are monogamous for life for many years and the pairs (a male and a female) raise their young ones.
- Pigeons and doves utilize piloerection, where they fluff up or raise their feathers to help regulate their body head.
- All the birds under the Columbidae family spend most of their time dustbathing, sunbathing, soaking, and bathing in water. They love preening in general.
- Members of the same species usually communicate by producing a variety of calls, songs, or gestures. This is a good indication of their social nature.
- Most doves and pigeons possess excellent navigation capabilities.
Lifespan
The estimated natural lifespan of pigeons and doves is 10 to 20 years. However, since wild birds usually face dangers like hunting, predation, and injury that cut off their lifespan, they may not achieve this lifespan.
It’s estimated that wild doves may live for as little as 2 years only while wild pigeons may live for 3 to 6 years. However, some wild birds may still be lucky enough to reach an older age.

Due to the proper care and feeding tamed doves and pigeons tend to enjoy from their handlers, they tend to live a bit longer than their feral counterparts do.
The oldest dove, Methuselah (a white-collared male dove) made an entry into the Guinness Book of Records back in 2004 having clicked an old age of 29.5 years (Source).
In 2013, Peace, a retired racing pigeon entered the Guinness Book as the oldest pigeon on the planet, having achieved an old age of 24 years and 188 days.
Flight capabilities
Both pigeons and doves are generally good flyers and can take up to the sky at the speed of an average car! However, pigeons seem to have much better flight capabilities compared to the doves.
For instance, the North American Mourning dove has recorded a speed of up to 55 mph (88 km/h) and the turtledove has recorded a speed of up to 37 mph (60km/h).

This dove speed is on the lower side compared to the pigeons, especially the homing racers, which can hit high speeds of between 50 and 60 mph (80 to 97 km/h). Some pigeons have even attained 90 mph (145 km/h) in pigeon races. (Source).
That said, not all pigeons are good flyers. Some wild pigeons like the Victoria crowned pigeon cannot fly great distances and only get off the ground to roost in trees.
Diet
All the birds under the family Columbidae are herbivorous and mainly eat seeds, grains, and fruits. As such, there are no differences between pigeons and doves when it comes to diet.

However, the bird family is further divided into several subfamilies with respect to the type of food preferences for different species.
The subfamily Columbidae (typical doves and pigeons) eat seeds and grains while the rest of the subfamilies are frugivorous.
Nest and breeding
Pigeons and doves tend to build simple, rough, loose nests that look like a shallow dish or platform made from twigs.
Both birds prefer building in similar spots such as trees, cliffs, crevices, ground (for ground species), and buildings (for collared doves and feral pigeons).
Sometimes, these birds may use abandoned nests made by other similar-sized birds.

Building a nest takes around 2-4 days and both males and females take part in it. During this period, the pair tends to get territorial as they actively their new nesting site as well as the surrounding areas.s
For the breeding part, all the Columbids lay 1-2 eggs (though they may lay 3 eggs in some rare cases).
The grain-eating species can lay more eggs while fruit-eating species lay only one egg. These eggs are usually white or buff colored and have no sports or markings.
The male and female take turns to incubate their eggs, though females spend more time on the nest. The incubation lasts for around 11 to 30 days depending on the species.
Conclusion
Doves and pigeons are the same type of bird and have no differences scientifically. However, due to human perception and culture, most folks tend to think pigeons and doves are completely different types of birds. Most folks interpret the doves as noble and elegant birds, a symbol of purity. Pigeons, on the other hand, are kept as pets, ornamental birds, or as food sources. They are considered trademarks of the urban areas and parks.
The birds that are referred to as pigeons are usually larger and stockier while doves are generally smaller. The pigeons also have straighter tails while those of doves are more fanned out. Other than these visual differences, the two birds share similar common traits, body shape, diet, nesting and breeding behavior, and even lifespan.






