The Pigeon’s Digestive System: How These Birds Process Their Food
The digestive system of pigeons helps in the breakdown of their ingested food and the absorption of nutrients. Ideas about this system are necessary to understand the relation of this system with their proper diet, sound health, survival, and reproduction ability.
Different enzymatic and mechanical breakdowns occur during the passing period of foods through the digestive tract of pigeons. Then, nutrient and water absorption occur in the ileum and rectum.
In this article, we will discuss the anatomy of their digestive system and the roles of pigeon digestive organs. You can also learn the necessity of proper avian nutrition and feeding habits. Therefore, keep reading till the end.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Digestive System
From the pigeon bird anatomy, you will find that its digestive system has two significant portions. The first is the alimentary canal, and the second is the digestive glands. Here are the description of these major parts:
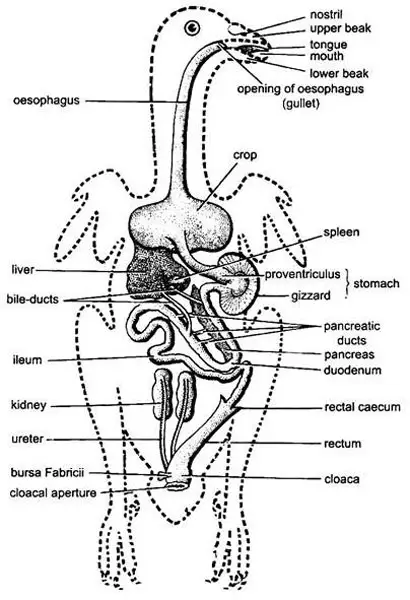
Alimentary Canal
The alimentary canal has three primary segments- stomodeum, mesenteron, and proctodeum. Let’s see their details:
1. Stomodeum
This portion of the pigeon digestive tract will consist of the following:
- Mouth: It’s the digestive tract’s opening, consisting of an upper and lower beak. These beaks help this bird to pick up its food.
- Buccal cavity: The floor of this part has a triangular-shaped tongue with a pointed edge. This tongue helps in manipulating and tasting the food.
- Pharynx: Generally, the function of the pharynx is to help in swallowing food.
- Gullet Or Esophagus: It is a thick-walled and wide tube joining the pharynx and crop. The gullet helps to carry the food from the pharynx to the crop.
- Crop: It’s a thin-walled and sac-like structure that primarily serves as a swallowed food reservoir. Also, the seeds get softer in this sac.
- Proventriculus: This is the anterior portion of the pigeon stomach. It can produce gastric juice, which will help break down food.
- Gizzard: It is the posterior chamber of the pigeon’s stomach. Secretion from its lumen will help in its digestive system.
Besides, the pebbles and stones inside the cavity will help grind and break the foods.
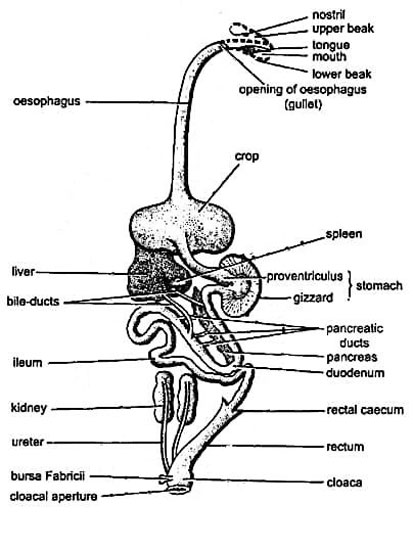
2. Mesenteron
It’s the small intestine of the pigeon, which has two significant portions- duodenum and ileum.
- Duodenum: It’s the U-shaped portion of the midgut. Besides, it will enclose the pancreas within its U-shaped portion.
- Ileum: It’s longer than the duodenum and has a coiled structure. Also, it has numerous villi, which can release several enzymes and increase the absorption area.
3. Proctodeum
In the proctodeum or large intestine, the last absorption of food takes place. Here are the parts of the proctodeum:
- Rectum: Through the rectum, the digested food is passed from the ileum to the cloaca.
- Cloaca: The cloaca has three significant chambers- coprodeum, urodaeum, and proctodaeum(large intestine). These chambers receive the rectum, genital and urinary ducts, and cloacal vents, respectively.
Digestive Glands
Here are details of a few digestive glands of pigeons.
- Buccal Glands: The function of buccal glands is to release amylase enzymes as well as mucus.
- Gastric glands: These glands are located at the proventriculus’s epithelial lining. They will produce gastric juice, which contains peptide enzymes.
- Liver: Two bile ducts will arise from the two lobes of the liver; both ducts will open at the duodenum. Both of them will secrete bile juice.
- Pancreas: There will be three pancreatic ducts for the secretion of enzymes into the duodenum’s distal limb.
- Intestinal Glands: These glands are mainly in the intestine’s epithelial lining and secrete several enzymes.
Therefore, the gastric motility of pigeons occurs through the organs of the alimentary canal sequentially. Typically, mechanical digestion takes place at the gizzard.
Alongside this, different enzymatic digestion will take place at the buccal cavity, proventriculus, and duodenum.
Pigeons have a distinguishing avian digestion process for digesting seeds. Their digestive system goes through several adaptations, which are:
- Seeds can get softened due to the crop function before going to the stomach
- Koilin secretion in the gizzard can cause the breakdown of food
- The small stones that pigeons swallow are accumulated at the gizzard. These stones help in the effective breakdown of the seeds by grinding
The Process Of Digestion
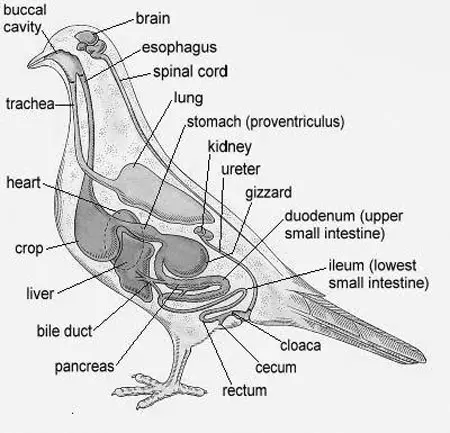
Here is a detailed description of the pigeon digestion process:
Step 1: As they lack teeth, after eating seeds, buccal cavity glands’ secretion like amylase enzyme and mucus will lubricate the seeds for ease of swallowing.
Step 2: The pigeon can store the food inside the crop for some time, which they can digest later.
Step 3: Inside the crop, water, body warmth, and autolytic action of bacteria will help to soften the seeds further.
Step 4: In the proventriculus, the gastric juice’s pectic enzyme will react with the food.
Step 5: In the gizzard, the mechanical breakdown will occur by the grinding action and muscular contraction.
Step 6: The secretion of pepsinogen and HCl inside the stomach will increase the acidity of food, and a little digestion will take place.
Step 7: Then, after coming to the duodenum, the partially digested food will meet with the intestinal secretion, pancreatic juice, and bile acid.
Step 8: In the duodenum, the complete conversion of carbohydrates, protein, and fat into diffusive micromolecules will take place. They happen as follows:
- Carbohydrate converts into glucose
- Fats will convert into fatty acid and glycerol
- Protein converts into amino acid
Step 9: These micromolecules can diffuse quickly through the ileum’s thin wall and then go into the blood flow.
Step 10: After the intestinal absorption, the residual food matter will pass through the rectum. During this time, the absorption of residual water in the matter will take place.
Step 11: After the water absorption, the dry and undigested portion of food will eject from the pigeon’s body through the cloacal vent.
Importance Of Proper Digestion
Pigeon’s health will significantly depend on their avian metabolism and digestion ability. Their sound digestive system will ensure their body receives nutrition from ingested food. Then, their metabolism will ensure that the received nutrition turns into energy properly.
Several consequences of digestive imbalance on pigeon health are:
- Dry mouth
- Loss of appetite
- Watery dropping
- Diarrhea
- Weakness
- Weak immune system
- Lose their competitive attitude
Factors Impacting The Pigeon Digestion

Several factors can impact the soundness of pigeon digestion. Those factors are:
- Frequent changes in the diet of pigeons can cause their digestive imbalance.
- Their excessive water consumption will increase the amount of water in their dropping.
- If pigeons ingest less amount of food, the physical volume of the fecal matter will be less than the urine. So the dropping will look watery.
- Excessive stress and hot or cold temperatures can cause an imbalance in the digestive tract.
- Different types of protozoa, viruses, and bacterial infections can also impact pigeon digestion.
The Importance Of Proper Nutrition

A proper and balanced diet will include protein, fat, carbohydrate, water, and minerals. Here is their role in pigeon health:
- Protein helps build organs, muscles, tissues, nerve systems, etc.
- The function of carbohydrates is to supply energy and maintain body warmth.
- Fat can also give energy to the body, which is almost two times that carbohydrate can.
- Minerals and vitamins help strengthen the immune system.
- Water functions to maintain the pigeon’s body temperature and carries oxygen and nutrients to cells.
Consequences Of Pigeon Malnutrition
The signs of poor bird health due to malnutrition are:
- Protein deficiency can cause their feathers to look dull, damaged, or discolored.
- Their skin may also look dull, dry, or itchy.
- Malnutrition is responsible for a weak immune system. So, pigeons become susceptible to various respiratory and gastrointestinal diseases.
- Due to malnutrition, their reproduction ability is also reduced. Also, they produce weak offspring.
Best Practice For Feeding Pigeons

If your pigeons are suffering from malnutrition or you want to prevent it from occurring, you must build up appropriate pigeon feeding habits. Here are a few tips for these according to the bird health institutions:
- Provide a balanced diet to your pigeons. You should serve them grains along with the seeds.
- Pigeon nutritional needs generally vary with the stages of their lifetime. So, make their diet plan and provide supplementary vitamins and minerals accordingly.
- A pigeon will need a minimum of 35 ml of water every day per 450 g of their weight. Try not to feed them excessively more or less water than this.
- Bird food manufacturers offer numerous pigeon diet formulations which you can serve to your pigeons to ensure their sound health.
- While a bird feeding process, pick high-quality food sources to ensure high nutrition only from an adequate amount of food.
Conclusion
Different portions of the pigeon digestive system will combine different enzymatic and mechanical processes that help them digest food.
Avian physiology research says that malnutrition can be responsible for their high mortality and smaller lifespan. Therefore, you must understand bird nutrition properly to understand this malnutrition issue better.






